Hardlink vs Softlink
In this article, we’ll talk about the difference between soft links and hard links, they might sounds simple and easy (in fact they are) but many engineers still don’t know the main difference between the two types,
To understand softlink and hardlink, we need to understand first Inode in Linux 🔑:
Inodes
Inodes are a data structure to store metadata about a file/directory,
in simple words, Whenever a user or a program refers to a file by name, the operating system uses that name to look up the corresponding inode from the Inode table, which then enables the system to obtain the information it needs about the file to perform further operations.
with that said, a file name in a Unix-like operating system is simply an entry in a table with inode numbers, rather than being associated directly with a file (in contrast to other operating systems such as the Microsoft Windows systems).
The inode numbers and their corresponding inodes are held in inode tables, which are stored in strategic locations in a filesystem,
now let’s discuss our main topic 🧐: hard link vs softlink
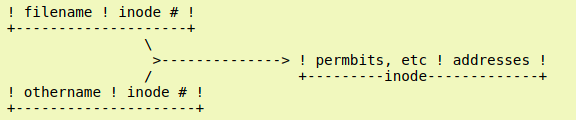
hard link
Two files are hardlinked, when both filename can reference the same inode number and thus the same content.
 \
\
To create a hardlink for the basic.file file :
ln basic.file hardlink.file\
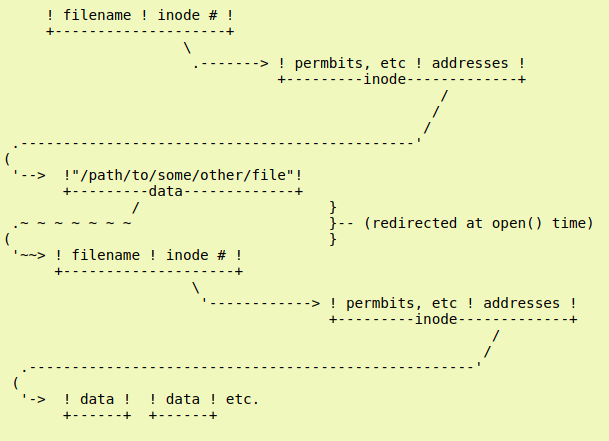
Soft link
The data part of this file carries a path to another file :
 \
\
To create a softlink for the softlink.file file :
ln -s basic.file softlink.file
Hope this helps ✅

Leave a comment